soils
Edaphic Scientific and SWAP Instruments collaborate on soil redox
In the realm of soil science and biogeochemistry research, the importance of accurate and real-time soil monitoring is paramount. Edaphic Scientific, a renowned provider of environmental monitoring solutions, has recently formed a strategic partnership with SWAP Instruments to extend comprehensive support for their cutting-edge soil redox probes in Australia and New Zealand. This collaboration marks…
Read MoreMonitoring of subtropical green roof water balance in Brisbane
Author: Sylvie Kunz PhD candidate, Green Infrastructure Research Labs (GIRLS), Cities Research Institute, Griffith University, Queensland, Australia Green roofs are a nature-based approach to help cities overcome the negative effects of urbanisation. By greening the cities, stormwater can be retained, the urban environment cooled, and habitats can be created. Monitoring of green roof water…
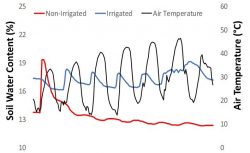
Read MoreReducing water inputs with on demand irrigation scheduling
New research has shown up to 40% reduction in irrigation can be achieved with soils or plant based decision making. Water resources are becoming increasingly expensive and scarce. To reduce costs and save on water, it is possible to alter irrigation scheduling (i.e. timing and dosing). Yet, when altering or decreasing irrigation it is critical…
Read MoreSap flow, evapotranspiration and irrigation management
Irrigating scheduling and amount can be accurately determined by combining sap flow (crop water use) sensors and evapotranspiration (ETo) data. This article outlines how growers, researchers or physiologists can use the Implexx Sap Flow Sensor, alongside the ATMOS 41 weather station, or the Implexx Evapotranspiration (ETo) station. Although this article has a focus on grapevines,…
Read MoreBushfires and assessing the risk of erosion
After a long season of bushfires in Australia, many of which are still burning, it is important to look forward to recovery and regeneration. There is much to do, measure and assess. Among these is the risk of soil erosion particularly where heavy rainfall, or high winds, impact bare ground. This article was first published…
Read MoreSap flow data show grapevines can tolerate extreme heatwave events
Monitoring sap flow on grapevines during extreme heatwave events has demonstrated that vines can tolerate extreme conditions when soil moisture levels were high. These results were found via the grapevine and heatwave monitoring project in the Riverina region of New South Wales (NSW), Australia. Heatwaves are “three or more days of high maximum and minimum…
Read MoreNew tensiometer-style sensor for avocado growers
A new, tensiometer-style sensor is improving irrigation management and saving time and costs for avocado growers. Irrigation monitoring and scheduling often relies on tensiometers – sensors that can measure soil water potential. Tensiometers are a favourite among avocado growers but they come with a huge problem: they are extremely tedious and odious to maintain. A…
Read MoreWhy this sensor has made the tensiometer and gypsum block obsolete
New and improved technology is now available for growers that is enabling more efficient and lower cost irrigation. The technology is a significant improvement on older, tensiometer and gypsum block style sensors by requiring zero maintenance, having a higher accuracy and being more robust. The technology is called the TEROS 21 Soil Water Potential Sensor…
Read MoreGrapevines, sap flow and heatwaves
Heatwaves can have a significant impact on grapevines, scorching leaves and decreasing growth and yield. Grape growers deploy various strategies to protect their vines during extreme heat events which can include spraying canopies with “sunscreen”. Although these strategies have merit, they often involve investment in additional infrastructure or are laborious to employ. Another strategy involves…
Read MoreWhy your soil moisture measurements are not accurate
Manufacturers of soil water content sensors supply their product with an output registering volumetric water content (VWC), typically expressed as a percentage. But where does this number come from and what does it actually mean? In all likelihood, the output value from the sensor will not be equal to the actual VWC of your particular…
Read More5 common mistakes when measuring soil moisture
Soil moisture, or soil volumetric water content, is easily measured with probes, sensors or handheld meters. These meters are as simple as pushing the probe or sensor into the soil, pressing read on the handheld meter, and you’re done. As easy as this appears, there are surprisingly many pitfalls and traps that can lead to wrong…
Read More